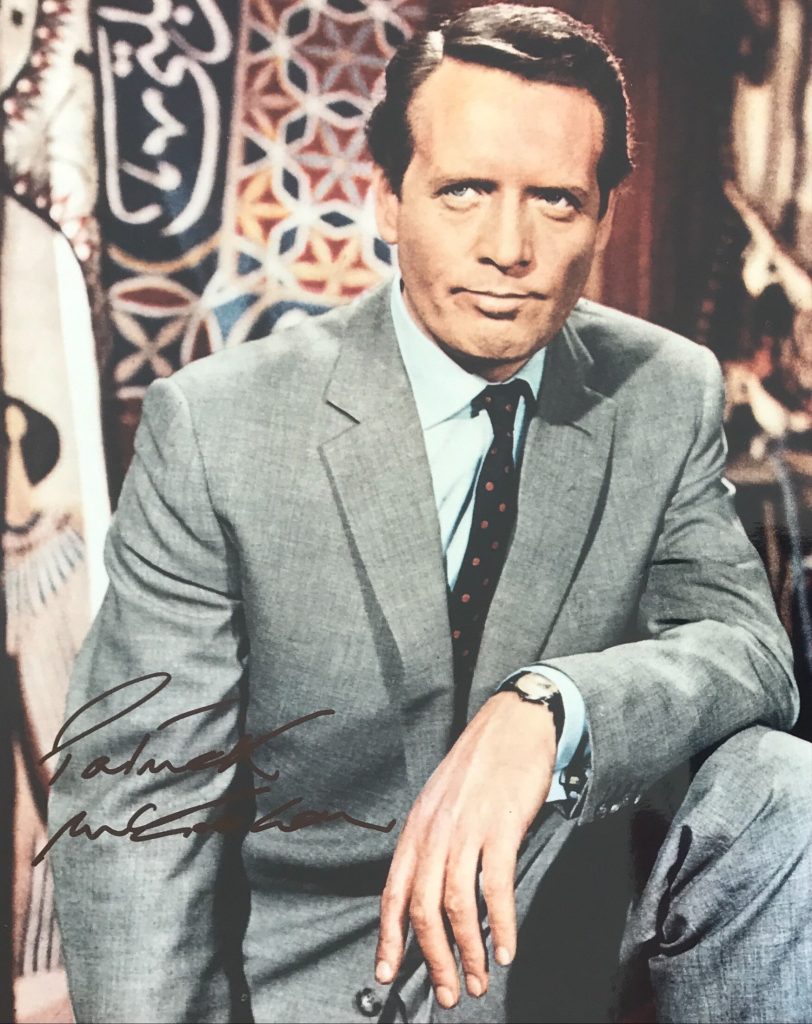
Patrick McGoohan acheived immortal television fame through his lead role in two cult British series of the 1960’s – “Dangerman” and “The Prisoner”. He was born in New York in 1928 and raised in Co. Leitrim, Ireland and then in Sheffield in the UK. He commenced his career on British films such as “Nor the Moon by Night” and “Hell Drivers”. In 1967 he went to Hollywood to make “Ice Station Zebra”. He made many high profile television appearances in the U.S. in the 70’s and 80’s and in 1995 he starred with Mel Gibson in “Braveheart”. He died in 2002.
“Guardian” obituary:
The handsome and steady-eyed Patrick McGoohan, who has died aged 80, was the star, co-writer and sometimes director of one of British television’s most original and challenging series of the 1960s, The Prisoner. In it, he played Number Six, a mysterious, resigned former secret agent who is always trying to escape from the Village, an apparently congenial community which is in fact a virtual prison for people who know too much. They are allowed to be comfortable there only if they conform completely and do not try to escape.
McGoohan was at the time, 1967, the highest earning British TV star, paid £2,000 a week through appearing in a highly successful secret agent series called Danger Man, in which he was John Drake, a European security man who – on McGoohan’s own insistence – never carried a gun or seduced a woman. But he was becoming disenchanted with the series, whose American purchasers from Lew Grade’s British television company ITC were pressing for more stock banalities such as car chases, shoot-outs and sex scenes.
He was invited to lunch with one American executive, who explained that they wanted pictures of him on the screen with glamorous girls – or, as McGoohan himself put it, “the corny showbusiness formula, the publicity machine grinding away”. He declined, and the lunch lasted only six minutes.
McGoohan, who had his own production company, Everyman Films, suggested to Grade a different, seven-part series for which he and others had prepared scripts, called The Prisoner. Grade cheerfully admitted that he had not understood a word of what McGoohan proposed, but had so much confidence in him that he agreed to fund it immediately.
Grade’s chief international customer, however, wanted a longer series. There were 17 Prisoner programmes, each of them loaded with mysterious psychological nuances, and set in an ideally artificial Village – in reality Portmeirion, an experimental community with exotic buildings designed by the architect Sir Clough Williams-Ellis, in north Wales.
From the opening titles, the programme was no easy ride. An angry secret agent drives into London in his fashionable Lotus 7 as a storm threatens, bursts into his boss’s office, throws his resignation down on to his desk, and storms out again. At home later, he finds an undertaker at his door. Gas comes through the keyhole, and he collapses as he packs his bags to go away. He wakes up in the Village, and no one will tell him where he is or why he is there, only that he is Number Six. ” I am not a number, I am a free man!” is his answer – and battle was joined in 17 attempted escapes.
In the series McGoohan met several sinister Number Twos but could never find out who Number One was until the last episode, improvised by McGoohan and his large writing team at the last moment, when Number One’s false face was pulled off to reveal a monkey’s underneath. When that too was pulled off, it revealed the face of McGoohan’s Number Six himself.
The implication that human beings can imprison themselves was timely in the swinging 60s, while at the same time the notion of the security services as the real enemy was seeping its way into fiction that had previously existed in more black and white terms. The programme achieved cult status for both itself and McGoohan personally, who had involved himself in all aspects of the productions in a way his colleagues thought obsessive. He became a darling of the campuses, but found that The Prisoner was a difficult act to follow.
In 1974, Everyman Films went bankrupt with debts of £63,000, at least half of it owed to the Inland Revenue. By the 1980s, McGoohan had recovered, The movie Kings and Desperate Men (1981) was praised by British critics and he starred on Broadway in Hugh Whitemore’s Pack of Lies.
The cosmopolitan variety of his professional interests owed something to his background. He was born in New York to parents who were once Irish farmers. His father, though barely literate, had an ear for Shakespeare, so that when Patrick read plays to him, he would remember and recite whole passages months later.
The family returned to Ireland when he was six months old and then, when he was eight, moved to Sheffield. Patrick later won a scholarship to Ratcliffe college in Leicester, where he played Lear in a school production. Leaving school at 16, he went to work in a wire mill, rising from the factory floor to the offices and then leaving to work in a bank.
This made him feel caged, so he set up instead as a chicken farmer, until an attack of bronchial asthma put him in bed for six months. He walked around Sheffield looking for work and eventually tried the Sheffield Repertory Company, for which he became assistant stage manager. When members of the cast were off sick, he was asked to step in, and found that he was best in the lighter Shakespeare plays, gaining praise for his Petruchio.
McGoohan stayed for four years, by which time he had appeared in 200 plays, including a touring production of The Cocktail Party in a small mining town, lit by miners’ lamps when the electricity failed. He met and married the actor Joan Drummond, with whom he had three daughters.
He made his first appearance in the West End in 1955 as the lead in Serious Charge. Orson Welles saw him there and asked him to play Starbuck in his production of Moby Dick Rehearsed. At the same time he stood in for Dirk Bogarde during a screen test, and was offered a five-year contract with Rank. But the studio’s “charm school” approach irked him and the contract petered out after four films.
After this, he turned more towards television and appeared in a production of Clifford Odets’s The Big Knife, about a paranoid Hollywood producer and the protege actor who he thinks has betrayed him. It was seen by Grade, who thought McGoohan ideal for John Drake in the Danger Man scripts. From 1960, McGoohan played in 86 episodes. At around this time, he turned down the chance to play James Bond in the first Bond movie, Dr No, seeing the Bond character as a stock gunman who treated women badly.
In 1968, when The Prisoner series was ending, McGoohan left Mill Hill, north London, to live in Switzerland after the local council refused him permission to fence his house off from prying eyes. In 1973 he moved to Pacific Palisades in California. There he wrote poetry, a novel and television scripts. He appeared in, wrote or directed some of the Columbo films in which his American friend Peter Falk appeared as the deceptively ruffled detective.
This redoubtable enemy of dumbing-down remained a highly individual operator into the 1990s. In 1991 he came to London to make the TV version of Whitemore’s play The Best of Friends, in which he played with considerable plausibility and élan another Irishman not frightened to swim against the tide, George Bernard Shaw. In 1995 he was cast as Edward I in Mel Gibson’s Braveheart.
In 2000, he provided the voice of Number Six for an episode of The Simpsons, and gained his last film credit in 2002 as the voice of Billy Bones in Treasure Planet. A proposed film version of The Prisoner has yet to make it to the screen, but a remake of the TV show has recently been filmed by ITV, with the US actor James Caviezel as Number Six, and is due to be transmitted later this year.
McGoohan is survived by his wife, three daughters and five grandchildren.
Patrick Joseph McGoohan, actor, writer and director, born 19 March 1928; died 13 January 2009
• This article was amended on Thursday 15 January 2009. Portmeirion is in north, not south, Wales. This has been corrected.
Dennis Barker’s obituary in “The Guardian” can be accessed here.